Electric vehicles (EVs), hybrid cars, and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) stand at the forefront of advancing cleaner, more sustainable transportation solutions. Each category embodies a distinct fusion of innovative technology, dynamic performance, and environmental benefits, tailored to meet a wide array of user requirements and inclinations.
Explores the differences among EVs, hybrids, and PHEVs, offering an in-depth analysis that draws on factual data and informed insights to elucidate their characteristics and contributions to the evolving automotive world.
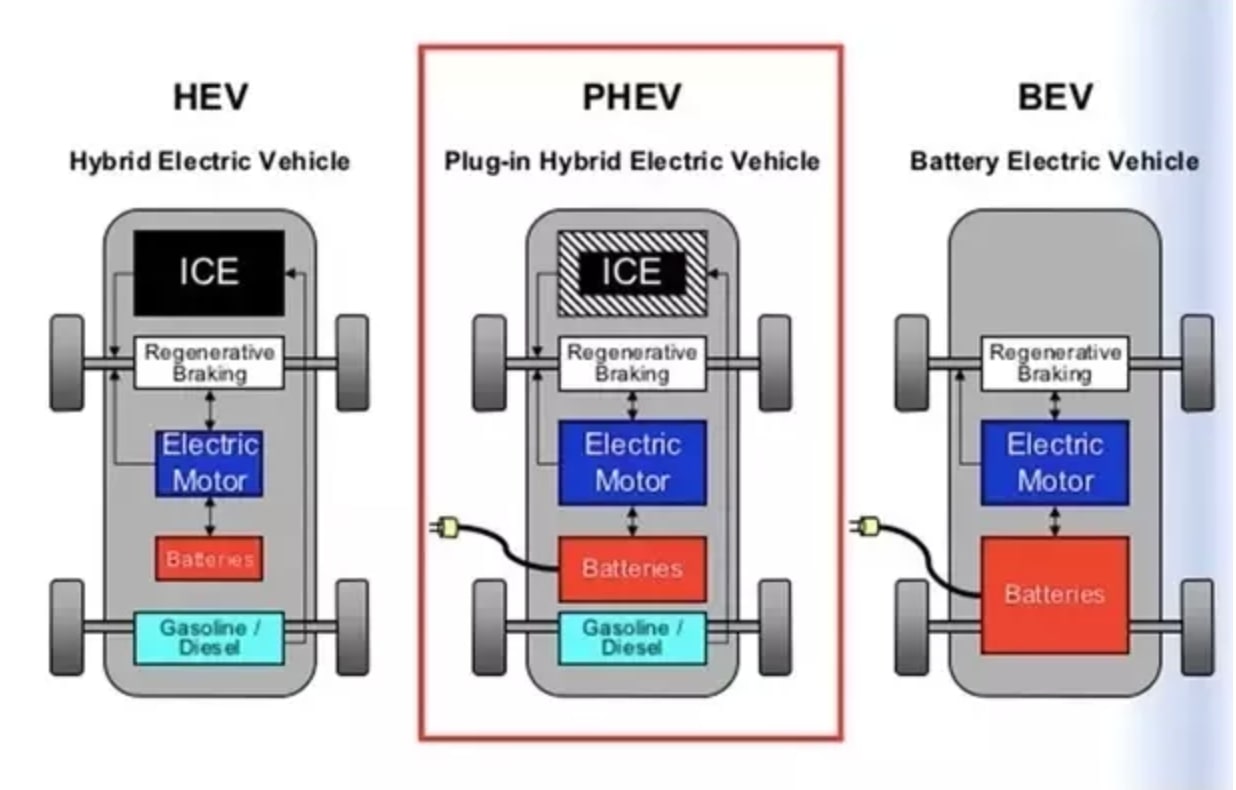
Electric Vehicles (EVs)

1. Definition and Technology
Electric vehicles (EVs) harness the power of electric motors to propel the vehicle, drawing energy from onboard rechargeable batteries. This design eliminates the internal combustion engine, relying solely on electrical power.
The absence of a conventional engine allows for a quieter, smoother ride, with the vehicle’s performance directly tied to the efficiency and capacity of its electric motor and battery system. The technology behind EVs is continually advancing, leading to improvements in battery life, motor efficiency, and overall vehicle reliability.
This shift represents a fundamental change in automotive engineering, emphasizing clean energy, reduced mechanical complexity, and innovative use of electronics for enhanced driving dynamics and energy management.
2. Environmental Impact
Electric vehicles offer a transformative environmental advantage by producing zero tailpipe emissions. This characteristic drastically reduces their environmental footprint compared to traditional vehicles, contributing significantly to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The environmental benefits of EVs extend further when charged from renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, enabling a truly sustainable transportation solution. By displacing the need for fossil fuels, EVs help mitigate climate change, reduce urban pollution, and decrease dependence on oil.
The broader adoption of EVs signifies a critical step towards achieving global environmental goals, such as reducing carbon emissions and combating air pollution.
3. Performance
The performance of electric vehicles is characterized by their instant torque delivery, which ensures rapid acceleration and responsive handling. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors generate peak torque from a standstill, enabling EVs to achieve fast and smooth acceleration immediately.
This instant power delivery is paired with a low center of gravity, afforded by the battery placement, enhancing vehicle stability, handling, and ride comfort.
The lack of traditional engine noise creates an exceptionally quiet driving experience, while the reduced number of moving parts lowers the likelihood of mechanical issues, potentially decreasing maintenance costs and increasing vehicle longevity.
4. Range and Charging
The driving range of electric vehicles has seen considerable improvements, with many current models capable of traveling over 300 miles on a single charge, addressing previous concerns about their viability for long-distance travel. The evolution of battery technology has been central to this progress, enabling higher energy density and faster charging capabilities.
However, the development of charging infrastructure is crucial to support the widespread adoption of EVs. Rapid charging stations are becoming more common, allowing drivers to recharge their batteries significantly in just minutes, enhancing the practicality of EVs for everyday use and long trips alike.
Despite these advancements, the availability of charging stations and the time required to recharge remain important considerations for potential EV owners, especially in regions where the infrastructure is still developing.
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, significantly reducing their environmental impact, particularly in urban areas where air quality is a major concern.
Reduced Operating Costs: Electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline, and EVs are more efficient overall, leading to lower cost per mile for operating the vehicle.
Low Maintenance: Without the complexity of an internal combustion engine, EVs have fewer moving parts, which means less wear and tear and potentially lower maintenance costs over the vehicle’s life.
Performance Benefits: Electric motors provide instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration and a smooth, quiet driving experience.
Energy Efficiency: EVs convert over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid to power at the wheels, compared to about 20% for gasoline vehicles, making them significantly more energy-efficient.
Incentives and Rebates: Many governments offer tax incentives, rebates, and other benefits for EV buyers, making them more affordable and encouraging adoption.
Renewable Energy Integration: EVs can be powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, further reducing their carbon footprint and contributing to overall sustainability.
Regenerative Braking: This feature allows EVs to recover energy during braking, which is stored in the battery and used later, enhancing overall efficiency.
Reduced Noise Pollution: Electric vehicles are much quieter than conventional vehicles, contributing to less noise pollution in urban environments.
Innovation and Advancement: The EV market is rapidly evolving, with continuous improvements in technology, infrastructure, and vehicle options, offering consumers a growing range of choices.
Disadvantages of Electric Vehicles
Limited Range: Many EVs still have a relatively limited range compared to gasoline vehicles, which can be a concern for long-distance travel.
Charging Infrastructure: Inadequate charging infrastructure can be a significant inconvenience, especially in rural or underdeveloped areas, leading to “range anxiety.”
Longer Refueling Time: Charging an EV, even with fast charging, takes significantly longer than refueling a gasoline vehicle, which can be inconvenient for users with a busy lifestyle.
Higher Initial Cost: Despite lower operating costs, EVs typically have a higher upfront price compared to traditional vehicles, although this is gradually changing as technology advances.
Battery Degradation: Over time, the batteries in EVs can degrade and lose capacity, which can reduce the vehicle’s range and overall performance and eventually necessitate expensive battery replacement.
Limited Model Variety: While growing, the selection of EV models, especially in certain segments like trucks or affordable compact cars, is still limited compared to gasoline vehicles.
Impact of Extreme Weather: Battery performance and, consequently, vehicle range can be significantly affected by very cold or very hot weather, potentially reducing the effectiveness of EVs in extreme climates.
Energy Source Concerns: If the electricity used to charge EVs is generated from fossil fuels, the overall environmental benefits are reduced, although this is improving with the growth of renewable energy sources.
Weight and Space: Batteries can be heavy and take up considerable space in the vehicle, which can affect vehicle design, handling, and interior space.
Recycling and Disposal: At the end of their lifecycle, the high-voltage batteries used in EVs present challenges in terms of recycling and disposal due to their chemical composition and potential environmental impact.
Hybrid Vehicles

1. Definition and Technology
Hybrid vehicles ingeniously integrate a gasoline engine with an electric motor and a battery, creating a synergistic system that enhances fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
The battery in a hybrid isn’t meant to be charged from an external source; instead, it garners energy through regenerative braking and the operation of the gasoline engine itself.
This regenerative process captures the energy typically lost during braking and converts it to electricity, storing it in the battery for later use.
The electric motor and gasoline engine work in tandem, with the motor capable of powering the vehicle alone at low speeds or assisting the engine during high-demand situations, thus optimizing the vehicle’s overall efficiency and performance.
2. Environmental Impact
Hybrid vehicles strike a meaningful balance in the automotive world by offering a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline cars, albeit with some emissions due to their internal combustion component. By supplementing the gasoline engine with an electric motor, hybrids achieve higher fuel efficiency and emit fewer pollutants.
Their eco-friendly prowess shines in urban settings where stop-and-go traffic allows regenerative braking to frequently recharge the battery, thereby maximizing the vehicle’s ability to operate on electric power alone or with minimal gasoline consumption.
This dual-mode operation significantly cuts down on fuel use and reduces greenhouse gas emissions, positioning hybrids as a practical green solution for city commuters and eco-conscious drivers.
3. Performance
A harmonious blend of efficiency and power characterizes the performance of hybrid vehicles. The electric motor enhances the vehicle’s operation, providing additional power during acceleration, which can reduce fuel consumption and improve the vehicle’s responsiveness.
This integration allows for smoother transitions between power sources, delivering a driving experience that is both efficient and enjoyable.
The immediate torque from the electric motor, combined with the sustained power of the gasoline engine, ensures that hybrids can maintain performance levels comparable to conventional vehicles while achieving better mileage and emitting fewer pollutants.
4. Convenience
One of the most appealing aspects of hybrid vehicles is their inherent convenience. They are designed to be as user-friendly as conventional cars, requiring no changes to the driver’s habits, such as the need for plugging in to recharge.
This self-sufficient charging capability through regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine means that the vehicle is always ready to go, providing peace of mind and eliminating the range anxiety associated with pure electric vehicles.
This ease of use, combined with the familiar operation and maintenance of a traditional gasoline engine, makes hybrids a compelling choice for consumers looking to reduce their environmental impact without compromising on convenience or altering their daily routines.
Advantages of Hybrid Vehicles
Improved Fuel Efficiency: Hybrids combine a gasoline engine with an electric motor, offering better fuel economy than conventional vehicles by alternating between these power sources or using them simultaneously for optimal efficiency.
Lower Emissions: By utilizing an electric motor to assist the combustion engine, hybrids emit fewer pollutants than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, contributing to reduced air pollution and a smaller carbon footprint.
Regenerative Braking: This technology captures energy usually lost during braking and uses it to recharge the vehicle’s battery, enhancing overall energy efficiency and extending the driving range.
Automatic Start/Stop: Hybrids feature automatic start/stop systems that shut off the engine at stoplights or during idle periods, saving fuel and reducing emissions, and then smoothly restart when needed.
Versatility: They offer the flexibility of gasoline-powered travel with the benefits of electric propulsion, such as reduced emissions and improved fuel economy, without the range anxiety associated with fully electric vehicles.
Tax Incentives and Rebates: Many regions offer financial incentives, including tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees, to encourage the purchase of hybrid vehicles, making them more accessible to a broader range of consumers.
Reduced Fuel Dependence: By using less gasoline than conventional vehicles, hybrids help reduce dependence on fossil fuels, contributing to energy conservation and energy independence.
High Resale Value: Hybrids often retain their value better than their gasoline-only counterparts due to their popularity, technological appeal, and lower running costs, benefiting owners in the resale market.
Performance Benefits: Many hybrids deliver a quieter, smoother ride compared to conventional vehicles, with instant torque from the electric motor enhancing acceleration.
Innovation and Choice: The hybrid market has grown significantly, offering a wide range of models, including sedans, SUVs, and trucks, catering to various preferences and needs.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Vehicles
Higher Initial Cost: Hybrids typically cost more than their non-hybrid counterparts due to the advanced technology and dual power systems, which can be a deterrent for budget-conscious buyers.
Complexity and Maintenance: The dual systems of gasoline and electric power can make hybrids more complex to maintain, and repairs might be more expensive or require specialized service centers.
Battery Replacement Costs: While not always a frequent concern, the potential need to replace the hybrid battery can be expensive, and battery performance can diminish over time.
Limited Electric-Only Range: Most standard hybrids can only drive a short distance on electric power alone, limiting the benefits of zero-emission driving.
Performance Perception: Some drivers may find hybrids less engaging or powerful than conventional cars, although this gap is narrowing with newer hybrid models offering improved power and handling.
Weight and Space: The addition of a battery pack and electric motor can add weight and take up space, potentially affecting the vehicle’s handling, cargo space, and interior room.
Towing Capacity: Hybrids, especially those not specifically designed for heavy-duty tasks, may have lower towing capacities compared to traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles.
Battery Disposal Impact: At the end of their life, the batteries used in hybrids can pose environmental challenges due to the materials and processes involved in their manufacturing and disposal.
Limited Model Options: While increasing, the variety of hybrid models, especially in certain market segments, is still more limited compared to the vast array of conventional vehicles.
Dependence on Fossil Fuels: Despite their improved efficiency, hybrids still rely on gasoline, meaning they are not completely free from the environmental impacts associated with fossil fuel extraction and consumption.
Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles (PHEVs)

1. Definition and Technology
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) represent a sophisticated fusion of electric vehicles (EVs) and traditional hybrid technology, equipped with larger batteries that can be externally charged, unlike conventional hybrids.
This unique configuration allows PHEVs to operate over extended distances on pure electric power, mirroring EVs, while also maintaining a gasoline engine for longer journeys or when the battery’s charge is low.
The ability to plug in and recharge the battery, often to full capacity overnight with a standard household outlet, empowers these vehicles with a versatility that is attractive to drivers looking for an eco-friendly transition from traditional internal combustion engines without committing fully to an all-electric system.
2. Environmental Impact
PHEVs hold the potential to significantly curtail vehicular emissions, particularly in daily commutes and short trips that can be accomplished within their electric-only range. By operating in all-electric mode, these vehicles emit zero tailpipe pollutants, drastically reducing their overall environmental footprint.
However, the presence of a gasoline engine means that it will generate emissions when operating in hybrid mode, especially once the battery is depleted.
The environmental efficacy of PHEVs is maximized when they are regularly charged, allowing for maximum utilization of their electric-only capabilities, thereby conserving gasoline and reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Performance
The dual capability of PHEVs to switch between electric power and gasoline engine operation offers a versatile driving experience. In electric mode, drivers can enjoy the quiet, smooth, and responsive performance typical of EVs, with the benefit of instant torque and swift acceleration.
When longer journeys exceed the battery’s range, the vehicle seamlessly transitions to using the gasoline engine, thereby eliminating any concerns about range anxiety associated with all-electric vehicles.
This flexibility ensures a consistent driving experience, with the electric motor enhancing efficiency and performance, even when the vehicle is operating in hybrid mode.
4. Charging and Range
PHEVs stand out for their extended electric-only range compared to traditional hybrids, typically offering 20 to 50 miles of battery-powered driving before the gasoline engine is needed. This range is sufficient to cover the daily commuting distance of most drivers, enabling significant fuel savings and reduced emissions.
The convenience of recharging the battery from home or public charging stations adds to their appeal, providing drivers with the flexibility to use electric power predominantly.
The adaptability to charge the vehicle’s battery externally, coupled with the capability to fuel up with gasoline as needed, makes PHEVs an exceptionally versatile option for a wide array of driving needs and preferences, bridging the gap between conventional hybrids and fully electric vehicles.
Advantages of Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles
Electric and Gasoline Flexibility: PHEVs offer the flexibility to run on electric power for short to moderate distances and switch to gasoline for longer trips, providing a versatile driving experience without range anxiety.
Increased Electric Range: Compared to conventional hybrids, PHEVs have larger batteries and can cover significantly greater distances using only electric power, often sufficient for daily commuting needs.
Reduced Emissions: When operating in electric mode, PHEVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which helps reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions and local air pollutants, especially in urban areas.
Fuel Cost Savings: Utilizing electricity for daily travel can significantly lower fuel costs, as electricity is generally cheaper than gasoline and electric motors are more efficient than internal combustion engines.
High Efficiency: PHEVs are designed to maximize energy efficiency, with features like regenerative braking that recaptures energy usually lost during braking, further improving overall efficiency.
Tax Incentives and Rebates: Many governments provide incentives for PHEV purchases, such as tax credits, rebates, and access to carpool lanes, making them an attractive financial option.
Versatile Charging Options: PHEVs can be conveniently charged from standard home outlets or public charging stations, offering flexibility and ease of use.
Performance Benefits: The combination of electric and gasoline power in PHEVs can deliver a smoother, quieter ride and instant torque from the electric motor, enhancing the driving experience.
Reduced Oil Dependence: By using less gasoline, PHEVs help decrease reliance on petroleum, contributing to energy diversity and stability.
Eco-Friendly Innovation: PHEVs represent a step forward in green technology, showcasing advancements in battery and hybrid technology and encouraging further developments in sustainable transportation.
Disadvantages of Plug-in Hybrid Vehicles
Higher Initial Costs: PHEVs generally cost more upfront than conventional vehicles and standard hybrids due to their advanced technology and larger battery packs.
Complexity and Weight: The dual drivetrains in PHEVs add complexity and weight, which can affect vehicle handling, performance, and interior space.
Charging Infrastructure Requirements: While PHEVs can be charged using standard outlets, optimizing their electric capability requires access to charging stations, which may not be readily available in all areas.
Longer Charging Times: Charging a PHEV can take several hours, especially with standard home charging equipment, which can be inconvenient for users needing quick turnaround times.
Limited Electric-Only Range: Although PHEVs offer a substantial electric-only range, it may not be adequate for long-distance drivers, who will then rely on gasoline power.
Maintenance Considerations: The dual systems (electric and gasoline) can lead to more complex maintenance requirements and potentially higher repair costs than conventional vehicles.
Battery Replacement and Degradation: Over time, the battery’s capacity may degrade, leading to reduced electric-only range and eventually the need for expensive battery replacement.
Environmental Impact of Batteries: The production and disposal of the large batteries used in PHEVs can have significant environmental impacts, including the use of rare earth elements and the challenge of battery recycling.
Performance Trade-offs: Some PHEVs may have compromises in performance, such as reduced acceleration or efficiency, when compared to fully electric vehicles or traditional hybrids.
Inconsistent Fuel Economy: The fuel economy in PHEVs can vary significantly based on driving habits, how frequently the battery is charged, and the proportion of miles driven in electric mode versus gasoline mode.
Conclusion
Choosing between an EV, hybrid, or plug-in hybrid depends on individual needs, driving habits, and environmental priorities.
EVs are best for those looking to maximize their environmental benefits and who have access to charging infrastructure. Hybrids are suited for drivers not ready to commit to charging but still looking to gain fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. PHEVs offer a compromise, providing electric-only driving for daily commutes with the flexibility of gasoline for longer trips.