In the age of digital transformation, laboratories are embracing a significant shift towards electronic notebooks (e-notebooks) to streamline research processes, enhance collaboration, and ensure compliance with evolving standards. Traditional paper-based notebooks, once ubiquitous in laboratories, are gradually being replaced by their electronic counterparts, offering a quantum leap in efficiency, data management, and accessibility. This article delves into the burgeoning realm of electronic notebooks, exploring their impact on research standards and the scientific community at large.
The Evolution of Laboratory Notebooks
Laboratory notebooks, an enduring fixture in the realm of scientific research, have played an integral role as custodians of experimental protocols, observations, and results. Traditionally, these notebooks took the form of meticulously filled-out bound paper volumes, often accompanied by carbon copies for backup. However, despite their efficacy in their era, paper notebooks were not without their limitations.
- Accessibility Challenges: The sheer volume of information stored within paper records made retrieving specific details a laborious and time-consuming task, hampering the efficiency of research endeavors.
- Data Integrity Concerns: Handwritten entries, susceptible to errors, alterations, and illegibility, posed significant risks to the integrity of recorded data, casting shadows of doubt over research findings.
- Collaboration Hurdles: The geographic dispersion of research teams rendered sharing paper notebooks a logistical nightmare, hindering real-time collaboration and impeding the pace of scientific discovery.
Acknowledging these inherent shortcomings, the scientific community embarked on a quest for digital solutions to revolutionize laboratory practices and usher in a new era of scientific exploration.
The Rise of Electronic Notebooks
Electronic notebooks, or e-notebooks, emerged as a technological panacea for the inefficiencies plaguing traditional paper-based systems. By digitizing record-keeping processes, e-notebooks offer a plethora of benefits:
- Efficiency: E-notebooks streamline data entry, searchability, and retrieval, enabling researchers to work more efficiently and focus on scientific inquiry rather than administrative tasks.
- Data Integrity and Security: Electronic records are inherently more secure and tamper-proof than their paper counterparts. Built-in authentication features and audit trails enhance data integrity and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Collaboration and Accessibility: Cloud-based e-notebooks facilitate seamless collaboration among researchers, regardless of geographical location. Real-time data sharing and version control mechanisms promote transparency and foster interdisciplinary collaboration.
- Integration with Analytical Tools: E-notebooks seamlessly integrate with analytical instruments and laboratory equipment, allowing for direct data capture and automated workflows. This integration minimizes transcription errors and accelerates data analysis and interpretation.
Key Features and Functionalities

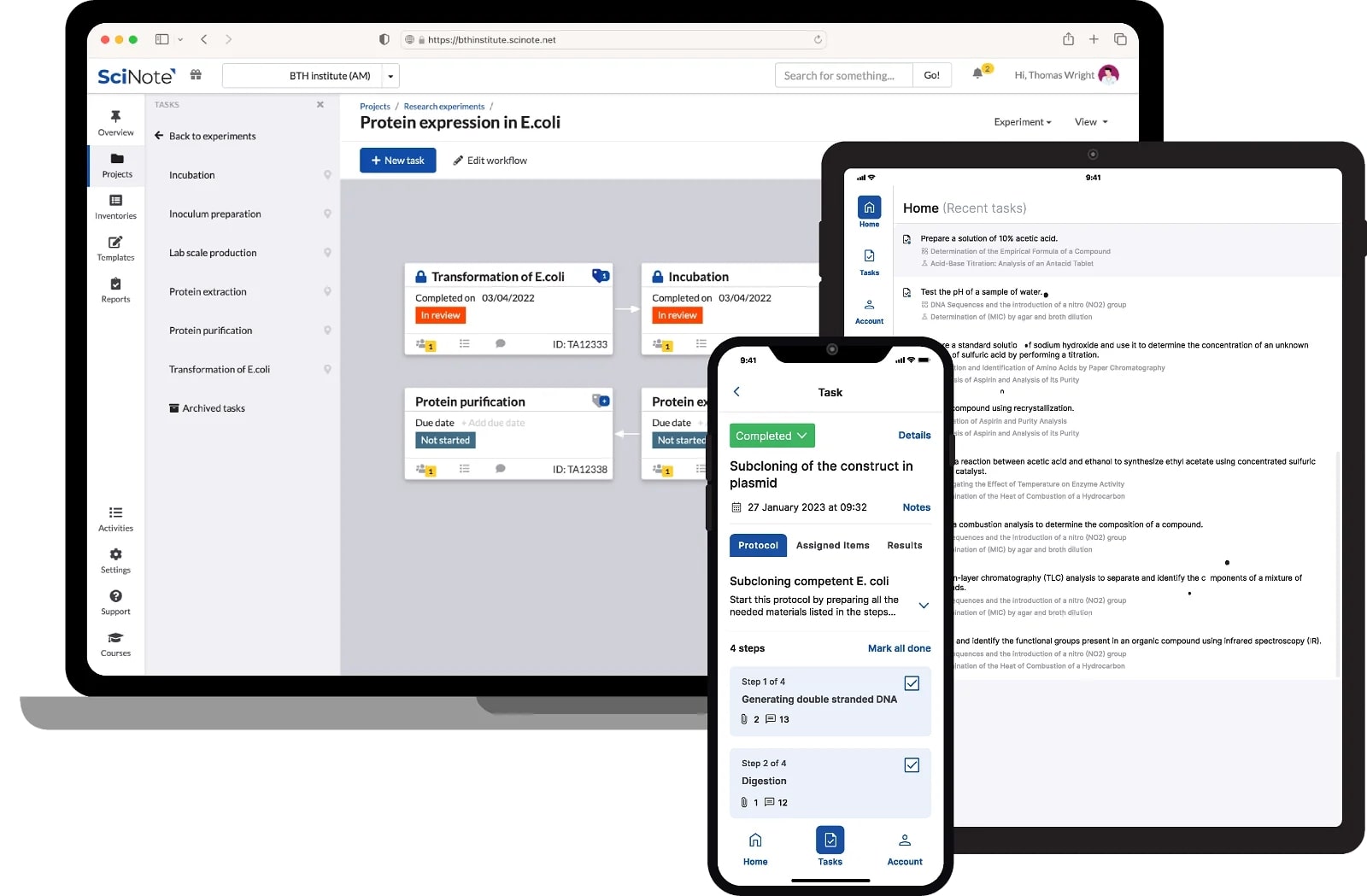
Modern SciNote ELN – Electronic Lab Notebook has evolved to become an indispensable tools for scientific research, offering a rich array of features and functionalities tailored to meet the unique demands of the research community. Let’s delve into an expanded discussion of these key aspects:
- Structured Data Entry: One of the pivotal strengths of e-notebooks lies in their ability to facilitate structured data entry. Researchers can employ customizable templates and forms, ensuring not only the systematic capture of data but also promoting consistency and standardization across various experiments. This not only enhances the accuracy of data collection but also lays the foundation for robust analysis and interpretation.
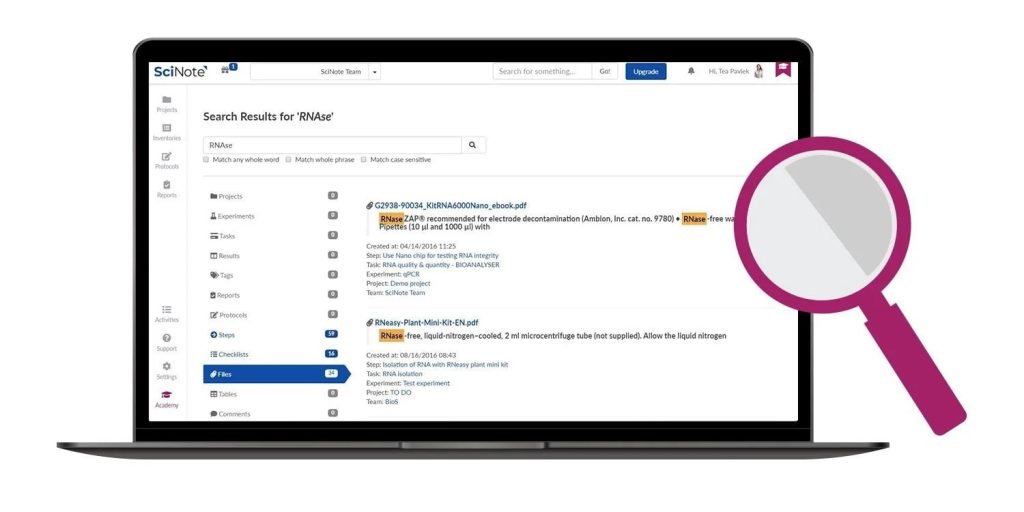
- Search and Retrieval: The power of modern e-notebook platforms extends to their advanced search capabilities and metadata tagging systems. These features empower researchers to swiftly retrieve relevant information from expansive repositories of experimental data. The efficiency gained in data retrieval significantly boosts productivity, allowing scientists to focus more on the analysis and interpretation of results.
- Version Control: Versioning capabilities are a cornerstone of e-notebook functionality. Researchers can meticulously track changes, revert to previous iterations, and maintain a comprehensive audit trail of experiment revisions. This not only ensures the integrity of the research process but also provides a valuable tool for quality control and reproducibility in scientific investigations.
- Electronic Signatures: Ensuring the authenticity and integrity of electronic records is paramount in the realm of scientific research. E-notebook platforms address this need through the incorporation of digital signatures and electronic witnessing functionalities. This not only meets regulatory requirements but also instills confidence in the reliability of the recorded data.
- Collaborative Workspaces: The collaborative nature of scientific research is well-supported by e-notebook platforms, offering researchers dedicated workspaces for collaboration. Within these spaces, scientists can seamlessly share data, annotate findings, and engage in threaded discussions in real-time. This fosters a dynamic and interactive environment, promoting knowledge exchange and collective problem-solving.
- Integration with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Seamless integration with LIMS and other laboratory software systems streamlines data transfer and enhances interoperability across laboratory workflows.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Adherence to regulatory standards and data integrity guidelines is paramount in scientific research, particularly in regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. E-notebooks play a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, including:
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11: E-notebook platforms offer features such as electronic signatures, audit trails, and data encryption to facilitate compliance with FDA regulations governing electronic records and signatures.
- Good Laboratory Practices (GLP): E-notebooks enable laboratories to maintain comprehensive, legible, and contemporaneous records of experimental procedures and results, thereby adhering to GLP guidelines.
- Data Security and Confidentiality: Robust data encryption, access controls, and user authentication mechanisms safeguard sensitive research data against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
While the adoption of e-notebooks promises transformative benefits, laboratories may encounter implementation challenges and resistance to change. To maximize the efficacy of e-notebook deployment, laboratories should consider the following best practices:
User Training and Support: Comprehensive training programs and ongoing technical support are essential to familiarize researchers with e-notebook platforms and mitigate user resistance.
Data Migration and Integration: Seamless migration of legacy data and integration with existing laboratory systems require careful planning and coordination to minimize disruptions to research workflows.
Customization and Scalability: E-notebook platforms should offer flexibility and scalability to accommodate diverse research needs and evolving regulatory requirements.
Change Management and Stakeholder Engagement: Effective change management strategies, coupled with stakeholder engagement initiatives, are critical to fostering a culture of innovation and embracing digital transformation within the organization.
Future Trends and Outlook
The rapid evolution of e-notebook technology promises to redefine research standards and revolutionize scientific inquiry in the years to come. Key trends shaping the future of electronic notebooks include:
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Integration of AI-driven analytics and predictive modeling capabilities will enhance data interpretation and decision-making in scientific research.
- Blockchain Technology: The adoption of blockchain-based platforms will further enhance data security, traceability, and provenance in laboratory record-keeping.
- Mobile Accessibility: Mobile-friendly e-notebook applications will enable researchers to capture data and access experimental records on the go, fostering greater flexibility and productivity.
- Interoperability and Data Sharing Initiatives: Standardization efforts and interoperability frameworks will facilitate seamless data exchange and collaboration across research institutions and disciplines.
Conclusion
electronic notebooks represent a quantum leap forward in laboratory research, offering unprecedented efficiency, data integrity, and collaboration capabilities. By embracing digital innovation and adhering to best practices, laboratories can harness the transformative power of e-notebooks to advance scientific discovery and shape the future of research standards.
As the scientific community continues to embrace digital transformation, electronic notebooks will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of innovation, driving breakthroughs in science and technology for generations to come.